ASSIGNMENT 8
Failure Mode and
Effects Analysis (FMEA)
Failure
mode and effects analysis (FMEA) is a team – based methodology for identifying
potential problems with the new or existing designs. It is the first step of a
system reliability study. FMEA is the core task in reliability engineering,
safety engineering, and quality engineering. FMEA involves reviewing as many
components, assemblies, and subsystem as possible to identify failure modes,
and their causes and effects. In order to determine the components of the
process that are most in need of change, FMEA includes the following steps:
1. Steps
in the process.
2. Failure
modes (What could go wrong?)
3. Failure
causes (Why would the failure happen?)
4. Failure
effects (What would be the consequences of each failure?)
Three factors that are considered in developing a FMEA:
1. The
severity of the failure.
2. The
probability of occurrence of failure.
3. The
likelihood of detecting the failure in either design or manufacturing, before
the product is used by the customer.
Different types of FMEA analysis:
1. Functional,
2. Design,
and
3. Process
FMEA.
Major benefits derived from a properly implemented FMEA are as follows:
1. It
provides documentation in selecting design with high probability of successful
operation and safety.
2. A
uniform documentation method of assessing potential failure mechanism, failure
modes and their impact on system operation, resulting in a list of failure
modes ranked according to seriousness of their system impact and likelihood of
occurrence.
3. Early
identification of single failure points (SFPS) and system interface problems
which may be critical to mission success and/or safety.
4. An
effective method for evaluating the effect of proposed changes t the design
and/or operational procedures on mission success and safety.
5. A
basis for in – flight troubleshooting procedures and for locating performance
monitoring and fault – detection devices.
6. Criteria
for early planning of tests.
Example of FMEA
analysis for car tire:
Keywords:
SEV – severity
OCC – occurrence
DET – Detection
RPN – Risk Priority
Number
Criteria for FMEA
Analysis
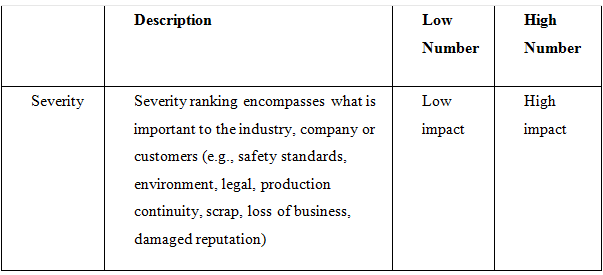
FMEA is analyzed based on three criteria:
1. Severity
effect on customer.
2. Occurrence
of failure.
3. Easy
to detect.
It is then ranked from 1 (low) to 10 (high) for each criterion.
Table 1: Severity,
Occurrence and Detection Ratings
Formula for RPN is:
RPN = severity x occurrence x detection



No comments:
Post a Comment